Contraindications. Body mass index (BMI) > 35 and anatomical features (e.g., trismus, mandibular prognathism) making laryngeal exposure difficult represent contraindications for this technique. Furthermore, this procedure is not indicated when a bulky tongue base pushes the epiglottis backward (secondary EC).
Explore This Issue
October 2022Postoperative Management. The Verbal Numerical Rating Scale 11 (vNRS-11) and Eating Assessment Tool 10 Italian version (I-EAT- 10) questionnaire were administered postoperatively. Patients were discharged on the first postoperative day with oral antibiotics therapy consisting of a third generation Cephalosporins (e.g., cefixime) once daily for seven days and a smooth and cold diet for seven to 10 days. Corticosteroid administration is not necessary. Patients were followed for at least six months postoperatively; endoscopic evaluation on the seventh and 30th postoperative days and PSG at three months were always performed.
RESULTS
From January 2016 to December 2020 we performed 536 surgical OSAS procedures, identifying a total of 109 patients with primary EC. Twenty-two patients underwent ESO within a multilevel snore surgery and were therefore ruled out, while 87 patients who underwent ESO exclusively fulfilled the inclusion criteria.
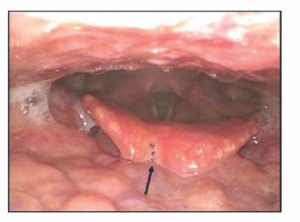
Figure 1. Postoperative onset of a notch of loss of substance caused by a vigorous manipulation of the epiglottis during the procedure. Example of improper healing of the epiglottis after an epiglottis stiffening operation
A strong prevalence of males was found; only 10 patients were women (11.5%), while 77 were men (88.5%); the mean age was 53.1 years old. The mean BMI was 26.8 kg/m2. Fourteen (16.1%) patients were affected by simple snoring and 73 (83.9%) patients were affected by OSAHS with a mean apnea/hypopnea index (AHI) of 30. The postoperative course of all patients was regular and substantially without pain, with discharge on the first postoperative day. Moreover, no patient had dysphagia, aspiration, or dysphonia. Two patients affected by diabetes mellitus had postoperative epiglottitis treated with oral antibiotics and resolved within six days. Postoperative fiberoptic endoscopic evaluation on the seventh and 30th postoperative days showed a consistent retraction of the epiglottis in all the patients. In three cases, loss of substance on the free edge of the epiglottis was found during the second postoperative examination (Figure 1). The mean postoperative AHI was 7.3, the mean postoperative snoring time was 11.2, and the mean Epworth Sleepiness Scale score was 6.3. Follow-up lasted from six to 68 months (see the supporting video.)