METHOD
DISE-PAP is utilized in patients >18 years of age with a diagnosis of obstructive sleep apnea who are intolerant of CPAP. In order to make DISE-PAP affordable in the clinical setting, supplies were purchased through the operating room, eliminating direct cost to the surgeon while also allowing for minimal increased patient billing.
Explore This Issue
October 2022The total cost of PAP supplies charged to patients for each DISE was $18.60. These fees were then bundled into the total hospital bill for the procedure. CPAP machines may be purchased online, and typically range between $300 and $1,500 depending upon make and model.
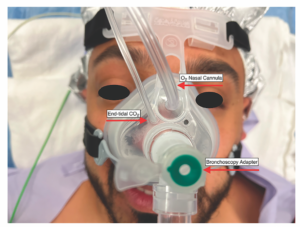
DISE PAP Assembly. In order to maximize clinical efficiency, the equipment may be assembled preoperatively by operating room staff (see supporting video). The CPAP machine is programmed to deliver a 5-minute ramp from 4 to 20 cm H2O. The proximal end of the CPAP tubing is inserted into the CPAP machine, and the viral filter is inserted into the distal end of the tubing. The mask is then assembled by removing the plastic 90° elbow from the mask and inserting the bronchoscopy adapter in its place. The oxygen tubing is inserted into the CPAP mask by cutting the distal end of an oxygen nasal-cannula tubing and inserting it into the mask. The end-tidal CO2 tubing is cut at a 45° angle and inserted into one of the pressure-release valves of the mask (Figure 1).
Drug-Induced Sleep Endoscopy. After a procedural timeout is performed, a bolus of propofol is administered and a steady infusion rate of propofol is initiated. While the TCI technique has been shown to provide a larger window of steady-state sedation, this is not available at our institution so a steady infusion rate over time allowed for a more consistent state of sedation. The nasal mask is then placed over the patient’s nose (Figure 1). Once secure, the flexible fiberoptic nasopharyngoscope is passed through the bronchoscopy adapter and into the naris predetermined to be less obstructed by septal deviation or other deformity. Once the patient reaches the appropriate depth of sedation, a formal upper airway evaluation is executed. Once the evaluation is complete, the CPAP tubing is connected to the mask via the bronchoscopy adapter and the CPAP machine is turned on to utilize the preprogrammed 5-minute ramp from 4 to 20 cm H2O. The airway is visually examined until complete resolution of airway obstruction and snoring is observed at the level of the soft palate, which was deemed the palatal opening pressure (JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2020;146:691-698). The pressure needed to resolve obstruction and snoring at the level of the lateral walls (lateral wall opening pressure, or LOP), tongue base opening pressure, and epiglottis opening pressure were also determined. The overall pressure needed to resolve complete upper airway obstruction and snoring was deemed the pharyngeal opening pressure (ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec. 2021;1-6). Upon completion of the sleep endoscopy, the flexible nasopharyngoscope is removed from the patient’s naris. The mask is then removed and the patient is returned to anesthesia. The average procedure time was 12 to 15 minutes. DISE PAP added approximately 5 minutes per case.