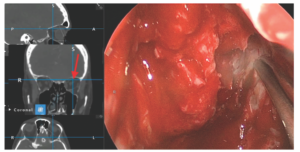
Figure 2. Endoscopic view with image guidance showing superolateral location of probe past the midpoint of the orbital roof.
For lateral supraorbital access, the lamina papyracea is carefully fractured away from the underlying periorbita. For anterior ethmoid arteries in close proximity to the skull base, removal of the lamina papyracea facilitates access so that the vessel can be controlled and divided. The posterior ethmoid arteries, sometimes with multiple branches, can also be controlled in a similar manner if encountered. The orbital contents can then be gently compressed, allowing superolateral access (Figure 2). All efforts should be made to keep the periorbita intact. Using a high-speed drill, skull base osteotomies can then be made at the appropriate location. Image-guidance software is helpful in this regard.
Explore This Issue
December 2022Once circumferential osteotomies are performed, dural incisions can be made and tumor removal can commence. Multi-layered skull base reconstruction followed by the vascularized extended nasoseptal flap is then performed.
RESULTS
The patient did well postoperatively, with improvement in her mental status. There were no orbital complications. Postoperative MRI demonstrated gross total resection.