Minimally invasive thyroidectomy achieves high cosmetic satisfaction and is not inferior to conventional thyroidectomy in terms of surgical results or perioperative complications.
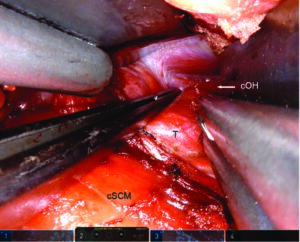
How To: Technique, Pitfalls of the Transaxillary Approach for Robotic Thyroidectomy
Advantages of thyroidectomy using transaxillary robotic surgery (TARS) are cosmetic, a high-definition view of structures, and a reduced risk of compressive cervical hematoma; the main drawbacks are the cost and duration of the procedure

What Is the Role of Transoral Thyroidectomy?
Transoral thyroidectomy can be safely performed in a select group of patients. Here are its unique advantages and guidance on when it should be used.
Older Age Associated with Voice, Swallowing Changes After Thyroidectomy
Older age is independently associated with the development of voice or swallowing changes after thyroidectomy.
Oncogene Panel Evaluation for ITNs Result in More Aggressive Surgical Management Techniques
OP evaluation was associated with higher rates of total thyroidectomy and central lymph node dissection without increasing the yield of malignancy or decreasing the rate of completion thyroidectomy
Patients with Graves Disease at Increased Risk for Hematoma Following Thyroid Surgery
Graves disease is the only indication in which patients undergoing thyroidectomy are at increased risk of postoperative hematoma formation
Pilot Project Validates Tool to Assess Thyroidectomy Skills
How valid, reliable and feasible is a tool developed at Johns Hopkins to measure the development of trainees’ operating room skills for thyroid surgery?
A Meta-Analysis of Minimally Invasive Video-Assisted Thyroidectomy
How does minimally invasive video-assisted thyroidectomy (MIVAT) compare with conventional thyroidectomy? Background: The advantages of minimally invasive thyroid surgery include shorter hospital stays, reduced postoperative pain, and improved cosmetic results. Studies […]
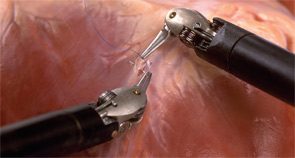
Scarless Surgery: The benefits and drawbacks of robotic thryroidectomy
Using robotic arms, surgeons can now remove the thyroid gland through an incision in the axilla, or armpit, thereby avoiding the large scar on the front of the neck caused by traditional thyroid surgery. The procedure offers no other benefits over the traditional approach developed a century ago by Emil Theodor Kocher, MD, according to head and neck surgeons who perform the robotic surgery. In fact, it takes longer to recover from the robotic surgery, they say, with some patients complaining of chest numbness for months afterwards.
The Impact of Thyroidectomy on Vocal Quality Characteristics
With no laryngeal nerve injury, do vocal characteristics change after thyroidectomy? Background: Vocal dysfunction is a feared complication of thyroidectomy. While operative injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve is a […]