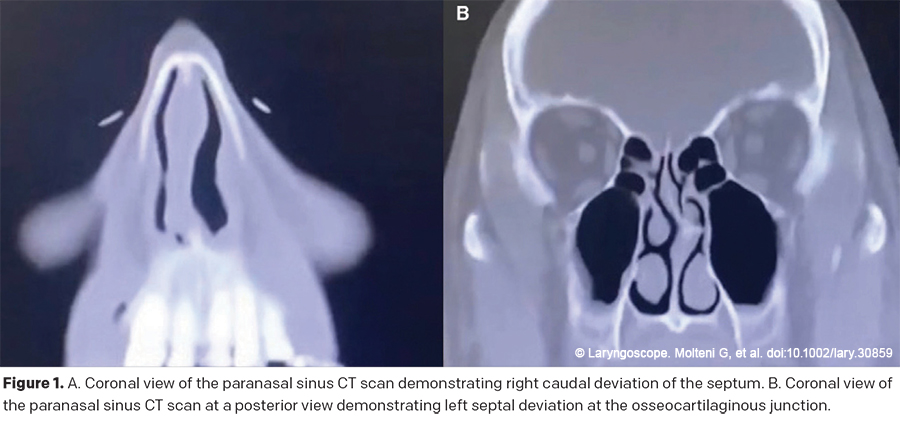
ENS represents one of the more complex conditions in otolaryngology, characterized by the paradoxical feeling of nasal obstruction despite objectively patent airways. In addition to the feeling of severe nasal obstruction—one patient called it “suffocating with every breath”—patients also report dryness, burning, and crusting. The quality-of-life impact can be so great that some patients travel the world seeking multiple consultations and revision surgeries.