In patients with high blood pressure resistant to treatment who also have obstructive sleep apnea, the more severe their OSA, the higher their blood pressure

Mild Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Children: What Is the Best Management Option?
Multiple therapeutic options may be effective for treating mild pediatric OSA including observation, management with anti-inflammatory medications, and surgery.
UAS Successful Treatment for OSA When Compared with TORS
Upper airway stimulation (UAS) is successful in treating obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) showing improved outcomes, length of stay, and readmission compared to transoral robotic surgery (TORS).
Air Pollution May Contribute to OSA
New data show that air pollution may contribute to obstructive sleep apnea.
Upper Airway Stimulation Effective for OSA in Patients with Prior Airway Surgery
Upper airway stimulation resulted in significant and profound improvement for all groups.
Multilevel Upper Airway Surgery Reduces Blood Pressure in OSA Patients
Upper airway surgery achieves a clinically significant decrease in systolic blood pressure and diastolic blood pressure in patients with obstructive sleep apnea.

Is Middle Ear Pressure Affected by Continuous Positive Airway Pressure Use?
Obstructive sleep apnea patients are likely to experience increased middle ear pressure from using a CPAP machine.
Powered Intracapsular Tonsillectomy Is a Safe Alternative to Traditional Tonsillectomy
PITA is a safe procedure that offers comparable disease control for children suffering from obstructive sleep apnea.
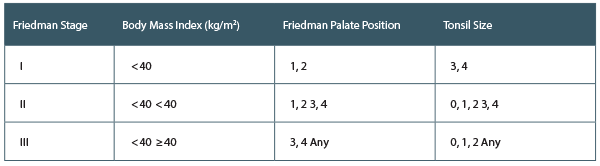
Is UPPP Effective in Obstructive Sleep Apnea?
There is level 1 evidence that suggests UPPP surgery is an effective treatment for OSA in the appropriately selected patient.
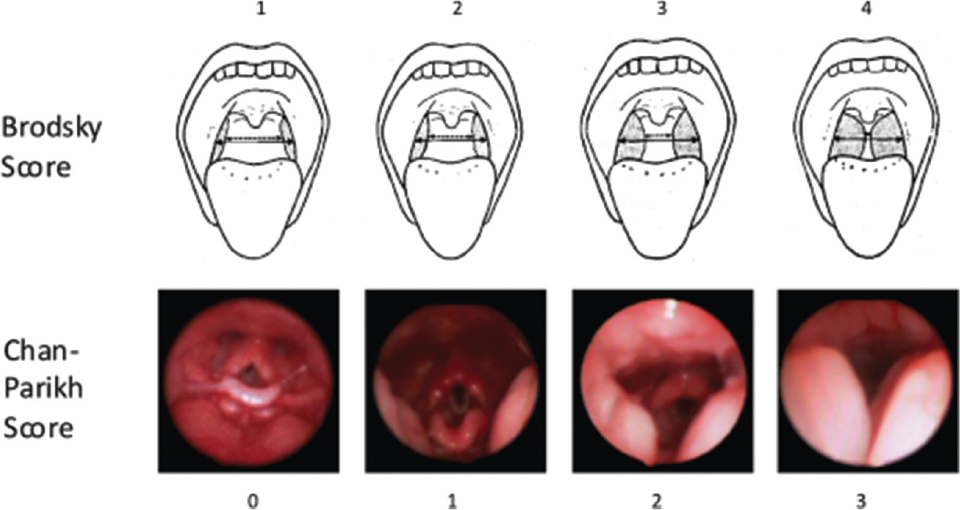
Adenotonsillectomy Alone May Not Be Enough to Treat Pediatric OSA
Children with small tonsils may not experience the same benefit and may have other sources of obstruction contributing to their OSA
- « Previous Page
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- …
- 7
- Next Page »