For patients with asthma and CRS, the addition of intranasal corticosteroids improved asthma symptoms and control as well as FEV1
ESS Improves CRS-Related Subjective Olfactory Dysfunction
ESS improves CRS-related subjective olfactory dysfunction with greatest gains seen in those with poorer CT scores at baseline
Eosinophilic Esophagitis, CRS Show Associations as Comorbid Conditions
An association between CRS and EoE as comorbid conditions suggests that a familial component is contributing to the etiology of both diseases
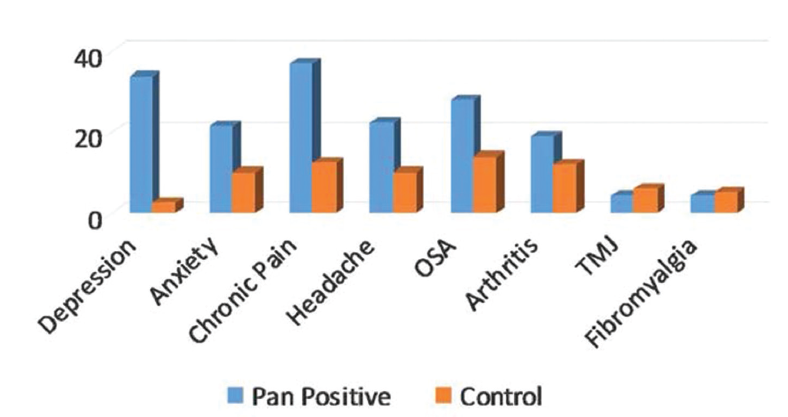
Pan-Positive Sinonasal Outcomes Test-20 Scores More Likely to Indicate Comorbidities in Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Depression, anxiety, headaches, and chronic pain more common in patients with all positive symptoms on the SNOT-20 score
Sleep Improves after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients With or Without OSA
Patients with chronic rhinosinusitis and comorbid obstructive sleep apnea see substantial improvements in quality of life following sinus surgery
Topical Antibiotic Use Following Sinus Surgery
Topical antibiotics are not recommended as first-line treatment for routine chronic rhinosinusitis
Snot-22 Scores Can Help Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis Considering Endoscopic Sinus Surgery
Chronic rhinosinusitis patients considering surgery should make decisions guided by their pre-operative QoL impairment, as measured using the SNOT-22
Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Cardinal Symptoms Change in Surgery, Medical Therapy
Endoscopic sinus surgery yields significantly greater improvement in cardinal symptoms compared with medical therapy alone
Change in Cardinal Symptoms of Chronic Rhinosinusitis Observed
Research measures symptom changes for patients with CRS undergoing surgery compared with those on medical therapy management

Drugs, Surgery, Endoscopic Sinus Surgery As Remedies for Chronic Rhinosinusitis
Guidelines to determine which patients are candidates for ESS when medical therapy fails