Antibiotic prophylaxis is effective when used in clean-contaminated oncologic surgery, but shouldn’t be used beyond 24 hours postoperatively


Antibiotic prophylaxis is effective when used in clean-contaminated oncologic surgery, but shouldn’t be used beyond 24 hours postoperatively

Routine use of prophylactics in clean otologic surgery is not supported by evidence, and their role in contaminated cases warrants more research

Long-duration therapy with macrolide antibiotics has been advocated for the treatment of recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). However, uncertainty exists as to which patients will respond to such treatment, the degree of benefit likely to be obtained, and the relevant risks to the patient and community at large

The clinical decision to treat or not to treat children with AOM remains controversial.
Have the characteristics of acute mastoiditis in children changed in the post-heptavalent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV7) era? Background: With the advent of antibiotics, the incidence of acute mastoiditis, a complication of […]
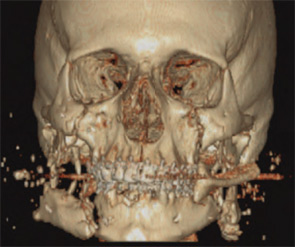
Ever since the first fully equipped otolaryngology team was sent to the Air Force Theater Hospital (AFTH) in Balad, Iraq in 2004, an otolaryngologist-head and neck surgeon has become a permanent member of any deployed multispecialty head and neck team, working alongside a neurosurgeon, ophthalmologist and oral and maxillofacial surgeon.


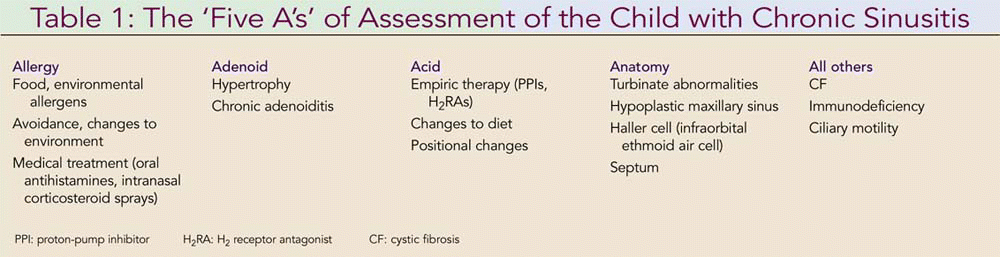
There are few data to support primary surgical reduction of the inferior turbinates in the pediatric patient.
