The literature supports dexamethasone as an effective agent for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting.


The literature supports dexamethasone as an effective agent for prevention of postoperative nausea and vomiting.

Questions remain regarding the ideal criteria for transfusion in these patients.
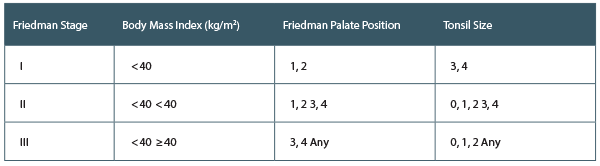
There is level 1 evidence that suggests UPPP surgery is an effective treatment for OSA in the appropriately selected patient.

Ampicillin/sulbactam is the preferred perioperative prophylactic antibiotic in major head and neck surgery.

Surgical intervention is indicated when patients have four to six episodes of acute sinusitis lasting four weeks or less each with asymptomatic periods in the interim.

There is little physiologic data comparing Eustachian tube function in each ear, but clinically relevant information can be gleaned from studies on surgical outcomes.

The overall incidence of esophageal secondary malignancies is low in patients with HNSCC

The use of neuromodulators appears to be helpful in patients with chronic idiopathic/ neurogenic cough

The incidence of alteration in taste sensation with coblation lingual tonsillectomy, TORS tongue-base reduction, and submucosal lingualplasty is sufficiently high to warrant warning patients.

The majority of recurrences occur within the first two posttreatment years