Environmental pollutants, such as second-hand smoke, chlorine in pools, and pesticides are associated with greater risk for allergies, studies report


Environmental pollutants, such as second-hand smoke, chlorine in pools, and pesticides are associated with greater risk for allergies, studies report

Is there sufficient evidence to continue to recommend this treatment for patients diagnosed with CRS?

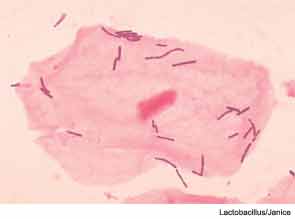
New research suggests that shifting bacterial populations may spur chronic rhinosinusitis
Nasal irrigation can be an effective therapy for chronic rhinosinusitis, provided patients—especially children—are shown safe and proper irrigation techniques
Activated hexose correlated compound (AHCC) and ginseng are some doctor-recommended, go-to complementary and alternative medicine treatments for patients with chronic sinusitis

Nasal dressings have frequently been advocated to improve wound healing and prevent ongoing bleeding after endoscopic sinus surgery (ESS). Initial experience focused on removable nasal packing materials; however, their adverse effect profile, such as pain/discomfort and mucosal trauma, has driven the development of absorbable biomaterials. Despite these developments, there is still little agreement on the optimal choice of nasal dressing or whether nasal dressings are required at all

Long-duration therapy with macrolide antibiotics has been advocated for the treatment of recalcitrant chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS). However, uncertainty exists as to which patients will respond to such treatment, the degree of benefit likely to be obtained, and the relevant risks to the patient and community at large

Otolaryngologists share their clinical observations on how to get the best results from using topical agents to treat chronic rhinosinusitis