This study aimed to describe operative techniques using rigid bronchoscopy and ferromagnetic bronchoscopic equipment to retrieve magnetic foreign bodies in distal tertiary bronchi beyond the reach of traditional optical instrumentation.
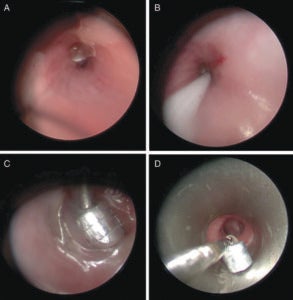

This study aimed to describe operative techniques using rigid bronchoscopy and ferromagnetic bronchoscopic equipment to retrieve magnetic foreign bodies in distal tertiary bronchi beyond the reach of traditional optical instrumentation.

TXA is increasingly used in otolaryngology to reduce intra-operative and post-operative bleeding, supported by evidence from emergency medicine and orthopedic surgery. Its safety profile is strong, and it is administered intravenously or orally, with emerging use in pediatric and adult otolaryngologic procedures.
Otolaryngologists charged with the care of infants affected by GERD should advocate for the avoidance of rice products in thickening feeds and opt instead for safe alternatives such as oatmeal, barley, wheat, and maize.

The BREATHE (Boosting REsources And caregiver empowerment for Tracheostomy care at HomE) study is a five-year, six-hospital trial that will advance understanding of how hospitals can better support caregivers of children with tracheostomies as they resume life, work, and family activities after discharge.
The topical beta-blocker timolol can be an effective first-line treatment for controlling symptoms of ulcerated IHs; however, its use should be carefully monitored.
Early adenotonsillectomy compared with watchful waiting and supportive care in children with mild sleep-disordered breathing (SDB) did not significantly improve executive function or attention at 12 months.
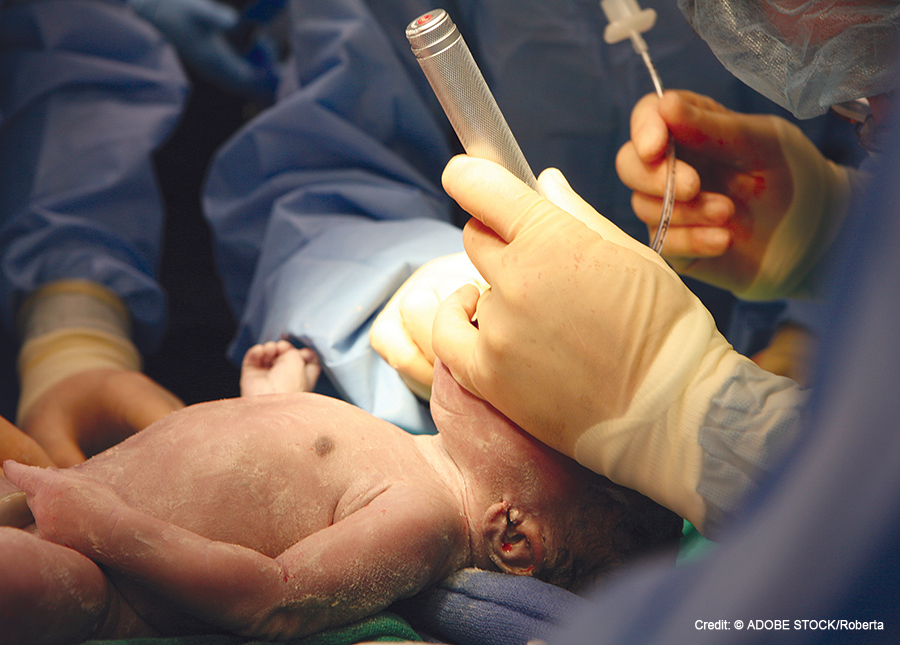
Using a video laryngoscope, versus direct laryngoscopy, when intubating infants can increase the odds of a successful intubation on the first attempt

A recent meta-analysis of six pediatric sinusitis studies demonstrated that antibiotics are effective in treating sinusitis in children

Social media is commonly used by physicians to share knowledge, provide medical education materials, and even seek peer advice. But is enough being done to protect patient privacy, especially for younger patients?