This conservative technique for treating nasal septal deformity in a newborn with a nostril retainer allows preservation of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus with consistent benefits in terms of postoperative morbidity.
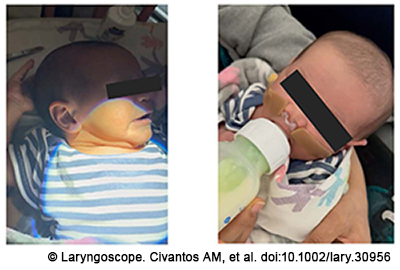

This conservative technique for treating nasal septal deformity in a newborn with a nostril retainer allows preservation of the medial wall of the maxillary sinus with consistent benefits in terms of postoperative morbidity.
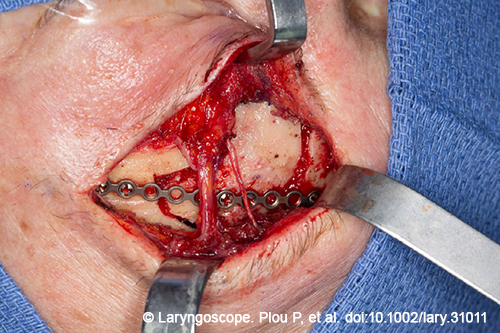
This full-extension eyebrow approach allows full exposure of the frontal sinus with a large osteoplastic bone flap and preservation of the supraorbital nerve.
The Procreate application was utilized on iPad Pro to intraoperatively annotate 3D renderings of head and neck surgical defects and resection specimens. By using Procreate on an iPad, the surgeon could annotate intraoperatively without breaking scrub to indicate the breadth of supplemental margins harvested in real time.
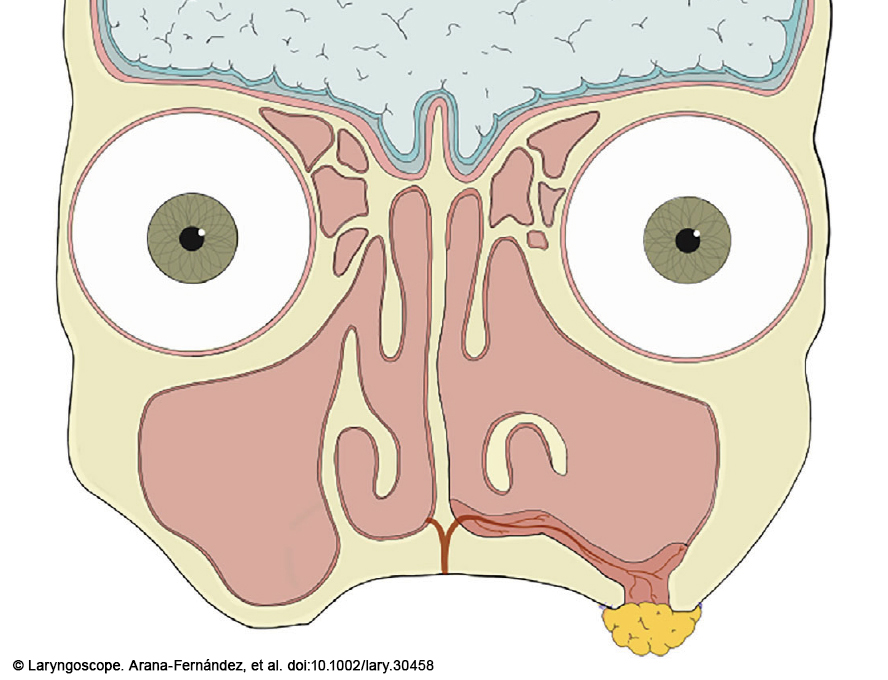
The aim of oroantral fistula management is to repair the defect, restoring the integrity of the sinus and oral cavity and preventing sinus infections.
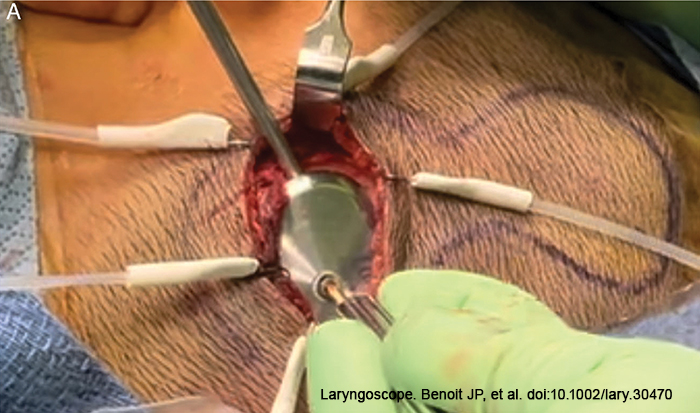
Minimally invasive OSIA 2 System reduces the risk of signal attenuation and skin complications, which were limitations of previous percutaneous and older transcutaneous devices.
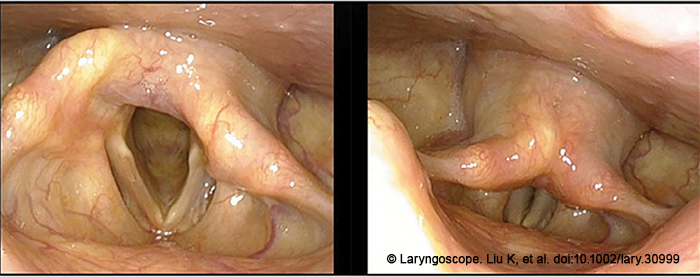
It is commonly accepted that early diagnosis and timely and effective joint reduction are the keys to treating arytenoid dislocation. In this article we take a look at a novel five-step reduction technique.
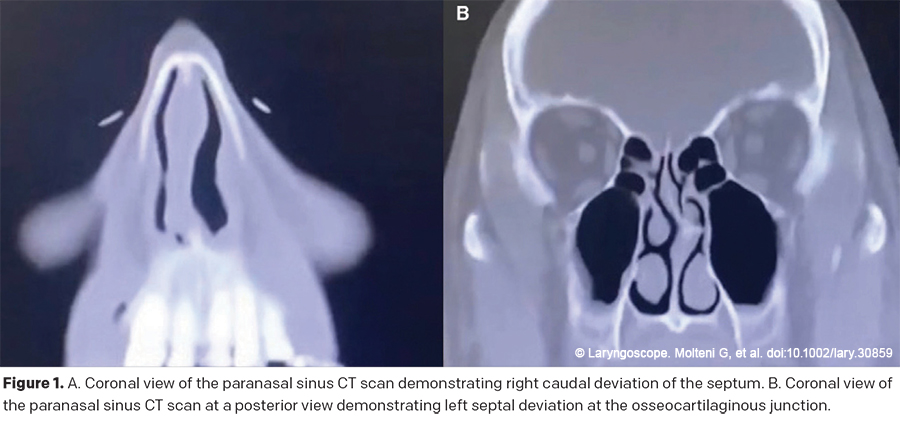
This article provides a detailed description of a dynamic endonasal columellar strut placement technique, as well as its clinical relevance and impact on patients after they have undergone routine septoplasty.
Up to 12% of all COVID-19 patients may need intensive care unit admission for severe interstitial pneumonia, with possible long-term endotracheal intubation for mechanical ventilation, but prolonged endotracheal intubation can lead to mucosal injury and inflammation, granulation tissue formation, perichondritis, and subsequent stenotic scar tissue development.
Should transoral options be limited or unavailable, recent reports have demonstrated success in closing oroantral fistulae with different intranasal mucosal flaps.
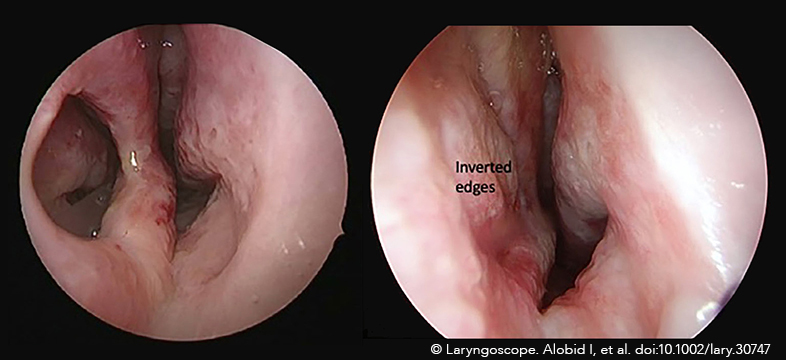
A recent survey demonstrated that respondents had a similar preference for the endoscopic and external rhinoplasty approaches, followed by the endonasal approach.