Observation following a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) for head and neck cutaneous melanoma (HNCM) is likely a reasonable approach to offer patients, as survival is unchanged in prospective clinical trials.


Observation following a positive sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) for head and neck cutaneous melanoma (HNCM) is likely a reasonable approach to offer patients, as survival is unchanged in prospective clinical trials.
Following free flap reconstruction, patient age correlated with development of a medical complication, and postoperative medical complications correlated with perioperative mortality.
The posterior septal nasal floor mucosal flap appears to produce good postoperative outcomes with reduced donor site morbidity.
There is a stepwise improvement in oncologic outcomes as surgical margin categorically improves from involved to close to clear.

Identification of sentinel lymph nodes (SLNs) in head and neck melanoma can be particularly challenging, due in part to the unpredictable and diffuse lymphatic drainage of the head and neck.
Preoperative imaging should be integrated with intraoperative findings based on endoscopic inspection and frozen sections in patients with maxillary cancer.

There is no conclusive evidence that extraction is required when a healthy tooth is present within the fracture line.

There are differences between how a community-based practice and a tertiary care center might approach head and neck cancer diagnosis. But what are they and why do they exist?

A liquid biopsy-based test to diagnose HPV-associated cancers may offer improved accuracy at a reduced cost and with a shorter time to diagnosis.
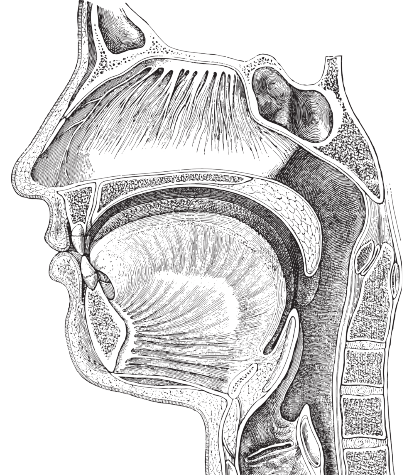
A thyroglossal duct cyst is one of the most common congenital anomalies of the midline neck.