Olfactory Impairment and Disease Etiology areLinked

Olfactory Impairment and Disease Etiology areLinked
Patterns of olfactory impairment do reflect underlying disease etiology
In children with DS, who have persistent OSA after T&A and lingual tonsil hypertrophy, LT significantly improved AHI, oAHI, and O2 saturation nadir
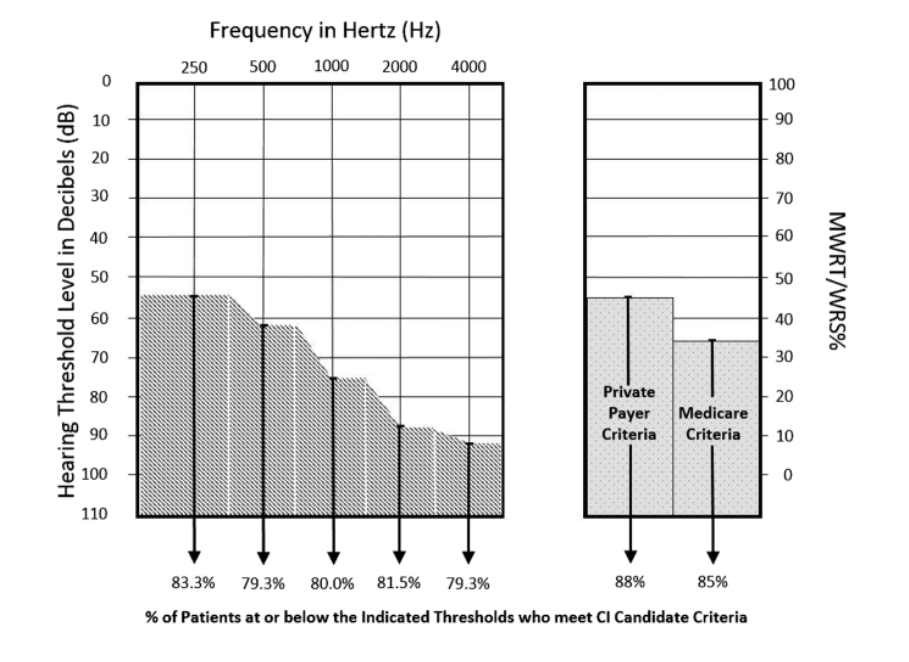
Routine audiometric findings can be used to identify patients who are likely to meet CI candidacy upon formal testing.
TORS BOT reduction decreases AHI and symptoms of sleepiness in adult patients with OSA
When stimulated by AHLs, T2R38 elicits calcium-dependent NO production that increases ciliary beat frequency and mucus clearance.
Comparison of surgeon outcomes of ESS is feasible, but must take into account a number of baseline patient characteristics
For patients with asthma and CRS, the addition of intranasal corticosteroids improved asthma symptoms as well as FEV1
ESS improves CRS-related subjective olfactory dysfunction with greatest gains seen in those with poorer CT scores at baseline
Placement of steroid-releasing sinus implants in the FSO significantly reduces the need for postoperative interventions in patients with CRS who are undergoing frontal sinus surgery