I have been a strong advocate of electronic medical records (EMRs) for almost a decade. In fact, I used the phrases “It is the silver bullet for health care reform infrastructure” and “It is the cornerstone for health care reform infrastructure” to describe EMR plans when President Obama was campaigning. However, technology, like fire, can warm your house or burn it down, cook your food or kill you. Likewise, the wrong EMR will escalate inefficiency and raise health care costs. The wrong mandates or the wrong incentives have the potential to paralyze the day-to-day practice of medicine.
Digital Dilemma: Physicians oppose EHR requirements
The federal government’s proposed rule establishing incentive payments for physicians who “meaningfully use” electronic health records (EHRs) is too onerous and would discourage physicians from participating, some otolaryngologists say.

Canal Wall Up vs. Canal Wall Down: Symptom of a greater need?
This issue of ENT Today includes an article on the debate over canal-wall-up (CWU) versus canal-wall-down (CWD) tympanomastoidectomy (p. 5). I remember hearing the same arguments when I was a resident at UCLA, which was also the last time I drilled a mastoid bone; my practice focused on head and neck surgery and pediatric otolaryngology. Over the past 32 years, Drs. Bruce Gantz, Rick Chole (two of my otology colleagues on the Board of Otolaryngology), and other otologist friends have suffered through my semi-tongue-in-cheek comments on why otologists can’t agree on which procedure is better. Although the technology used in both procedures has evolved, the final product of the two procedures, a dry, safe ear, is, as best I can tell, the same as it was when I was a resident. I have been told that one of the main factors considered in the decision regarding which procedure to perform is where the otologist trained.
A Partner in the Business: Practices see mid-level providers as valuable additions
When Winston C. Vaughan, MD, told his Stanford University patients he was leaving academia to establish a private group practice, they had one question: “Are you taking Kathleen with you?” Their concern attests to the integral role that Kathleen Low, RN, NP, fills as a patient-care provider in Dr. Vaughan’s otolaryngology practice.
Avoid the Hot Seat: How to prepare for a CMS audit
In February, the Centers for Medicare and Medicaid Services (CMS) began rolling out its national Recovery Audit Contractor (RAC) program, aimed at ferreting out improper payments and preventing fraud, waste and abuse in the Medicare system. If you bill for Medicare fee-for-service, you are fair game for a RAC audit. A three-year demonstration of the RAC program, which ended in March 2008, heavily targeted bronchoscopy, injectable drugs and IV hydration therapy. But auditors are rapidly expanding the list, and the permanent program will include adenoidectomies, tonsillectomies, thyroidectomies and other otolaryngology-related procedures.

Show Me the Evidence: Comparative effectiveness research could aid treatment decisions
A push at the national level to fund more comparative effectiveness research could mean more information for otolaryngologists about which treatments work best for a given condition and in which patients.
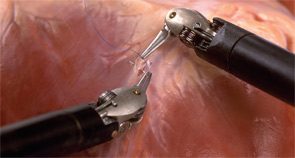
Scarless Surgery: The benefits and drawbacks of robotic thryroidectomy
Using robotic arms, surgeons can now remove the thyroid gland through an incision in the axilla, or armpit, thereby avoiding the large scar on the front of the neck caused by traditional thyroid surgery. The procedure offers no other benefits over the traditional approach developed a century ago by Emil Theodor Kocher, MD, according to head and neck surgeons who perform the robotic surgery. In fact, it takes longer to recover from the robotic surgery, they say, with some patients complaining of chest numbness for months afterwards.

A New Game Plan: Otolaryngologists and consultants devise solutions to ride out the recession
Otolaryngologists understand that even their most loyal patients, with finances ravaged by the lingering economic recession, may postpone or forego endoscopic sinus surgery, tonsillectomy or a chemical facial peel in favor of paying the mortgage.

Health Care as a Commodity: Competition should be focus of health reform, lecturer says
Donald Palmisano, Esq., MD, believes the key to curing the health care crisis in the U.S. involves respecting the sacredness of the doctor-patient relationship and capping the size of malpractice awards.

Digital Efficiency: Panel discusses the inevitability of EMRs
Electronic medical records (EMRs) are costly and require significant staff time to implement but have the potential to bring huge benefits to patients and doctors alike, said speakers at the Triological Society’s Combined Sections Meeting held here Feb. 4-7.
- « Previous Page
- 1
- …
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- …
- 27
- Next Page »