At first glance, the Otolaryngology Surgery Simulation Center at Montefiore Medical Center in New York resembles a traditional temporal bone dissection lab.


At first glance, the Otolaryngology Surgery Simulation Center at Montefiore Medical Center in New York resembles a traditional temporal bone dissection lab.

With the advent of fiberoptic and distal-chip scopes and other innovations, otolaryngologists are now able to perform many laryngeal diagnostic and therapeutic procedures on awake patients in the in-office setting rather than on fully anesthetized individuals in the operating room.
Do you cringe when another journal comes in, only to join the growing stack of still-unread back issues?
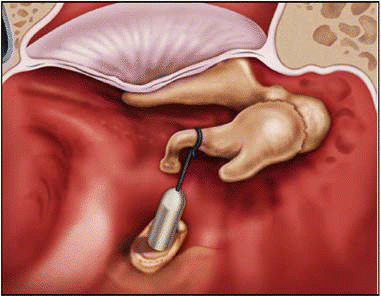
Be careful not to be too quick to say that a patient’s problems are due to canal dehiscence.


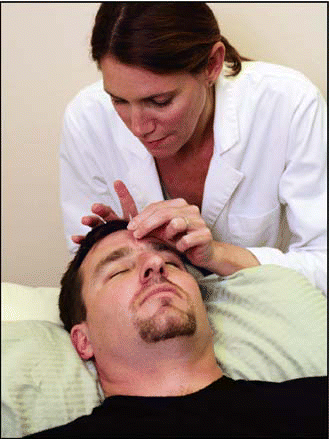
Patients with head and neck cancer treated with surgery and/or radiation often experience pain, shoulder dysfunction, and xerostomia.
Periodically, newspapers and journals perform readership surveys to determine the readers’ opinions of the publication.
Eosinophils are the bane of nasal mucosa, and no one knows better than Fredrick A. Kuhn, MD, of the Georgia Nasal and Sinus Institute in Savannah, GA-a region where it is not uncommon for otolaryngologists to see patients presenting with polyps.
Intraoperative volume CT is showing promise as a tool to help with complex endoscopic sinonasal and skull base procedures.