Academic medical centers within the United States bear the primary responsibility for promulgating and performing life sciences research.


Academic medical centers within the United States bear the primary responsibility for promulgating and performing life sciences research.

Generosity was the main topic of the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery’s 2007 John Conley Lecture on Medical Ethics by Rev. William G. Enright, PhD, Executive Director of the Lake Family Institute on Faith and Giving at the Center on Philanthropy, Indiana University, at the opening ceremony of this year’s annual meeting.
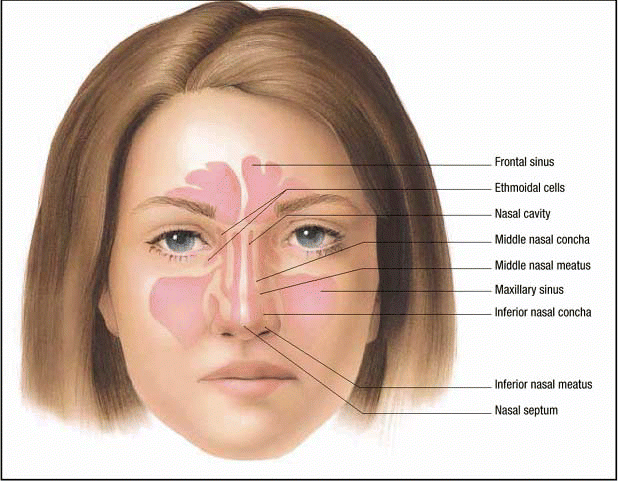
At its annual meeting, the American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery released its long-awaited multispecialty practice guidelines for treatment of adult rhinosinusitis.


How will 21st-century otolaryngologists meet these challenges?

A conservative approach to treatment of patients with squamous cell carcinoma from unknown head and neck primary cancers compares favorably with results of other reported more aggressive protocols utilizing comprehensive irradiation or concurrent chemoradiation, according to study results reported by Rajan S. Patel, MBChB, MD, April 29 at the American Head and Neck Society’s program during the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meeting.

As reported previously in ENToday, as many as 18 million Americans might have obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) with an apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) > 5.0 events per hour of sleep, according to the National Commission on Sleep Disorders Research report, Wake up America: A National Sleep Alert.


Neonates with younger gestational age and lower birth weight are more likely to fail extubation and to require earlier surgical airway intervention, according to an April 28 presentation by University of Texas Medical School, Houston, researchers at the American Society of Pediatric Otolaryngology program at the Combined Otolaryngology Spring Meeting.
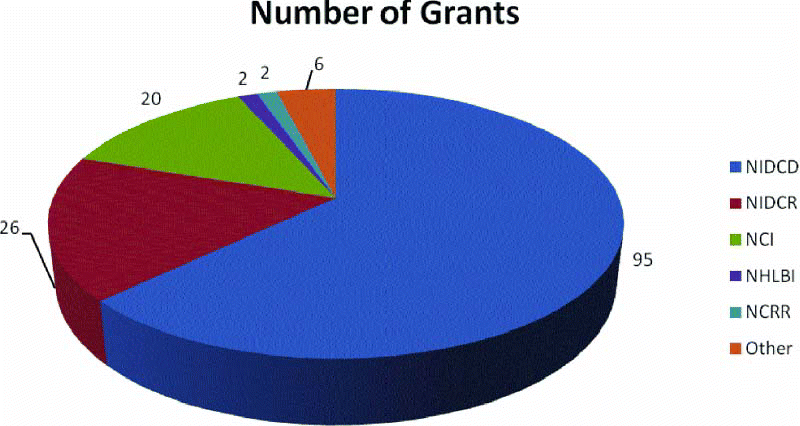
In the past, almost all support for otolaryngology research was provided through the National Institute on Deafness and other Communication Disorders (NIDCD) or its parent institute, the National Institute on Neurological Diseases and Stroke (NINDS).