There were no changes to the T (the size and location of the primary tumor) category, but many changes to the N (nodal) category. A clinical N1 designation will mean one or more ipsilateral lymph nodes, none greater than 6 cm; a clinical N2 will be contralateral or bilateral lymph nodes, none more than 6 cm; and clinical N3 will be lymph nodes larger than 6 cm.
Explore This Issue
June 2017Pathological N1 will be metastasis in four or fewer lymph nodes, and pathological N2 will be metastasis in more than four lymph nodes. There will be no pathological N3 category.
(click for larger image)
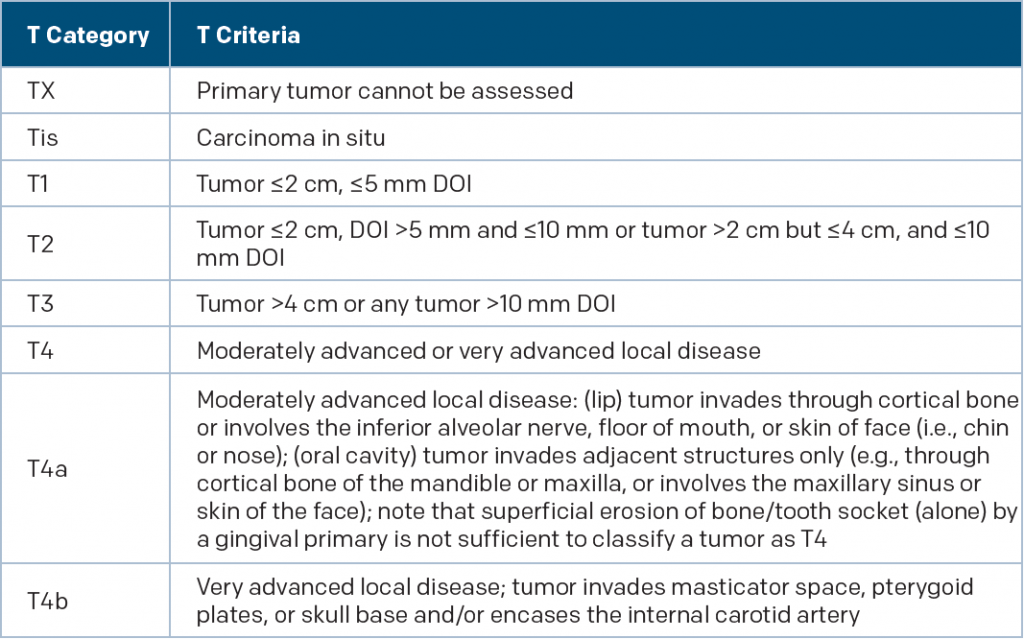
New T Category Criteria for Oral Cavity Cancer
DOI is depth of invasion and not tumor thickness
Source: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer; 2017
Dr. Kraus acknowledged this might make for tricky conversations between patients and clinicians, who will have to “try to tell [patients] that what is stage IV disease as we sit here in 2017 really is stage I or stage II. And it does create some challenges.”
He added that smoking was not included in the staging system, despite the evidence suggesting its effect on risk because the data were just not strong enough yet to build it in. He anticipated it would be incorporated in the next edition.
Mucosal melanoma: Dr. Kraus said the main change here was an acknowledgement of the poor outcome that most patients tend to have with this disease. There will no longer be a T1 or T2 classification, only T3, T4a, and T4b, because the outcomes are just too dire, he said. Eliminating those levels is “one of the rare times this has ever occurred in the AJCC,” he added.
“Because of the universally poor outcome, I think this an appropriate amendment. Even when you are stage 3a, you have anticipated survival that’s approximately 40%, and as you get into the 4c you ultimately approach zero over time,” Dr. Kraus said. “In spite of our efforts, this population of patients continues to do poorly.”
Unknown primary that is p16-negative: Dr. Kraus pointed out that most unknown primaries end up being positive for p16 protein, associated with HPV positivity, but that this staging involves only the p16-negative variety. A notable change in this area is that the pathologic extranodal extension (ENE) is broken into two segments: “micro” ENE with extension of no more than 2 mm, and “major” ENE with extension of more than 2 mm. Pathological ENE will increase the N stage by one level from the previous system, he said.