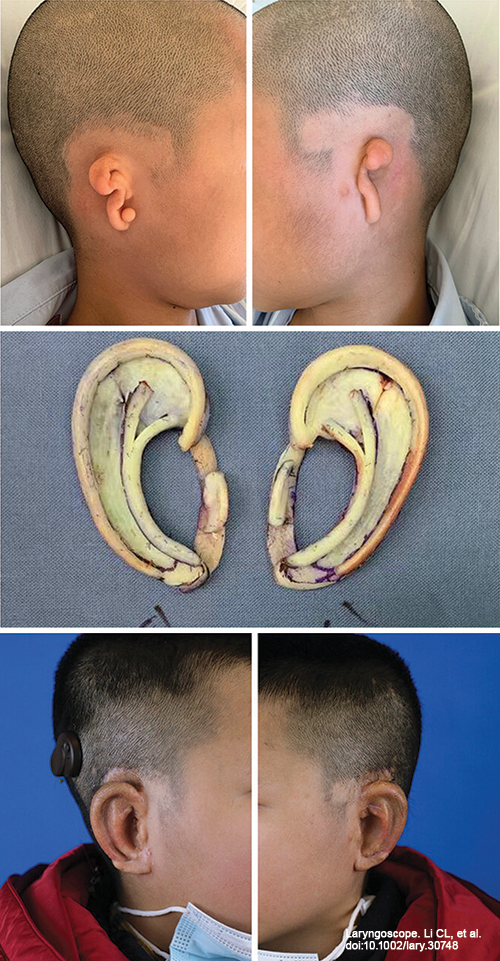
Figure 2. Simultaneous surgical treatment of bilateral microtia. (Above) A 9-year-old boy with bilateral lobule-type microtia. (Center) Bilateral fabricated frameworks at first stage surgery. (Below) Postoperative view after auricular elevation.
In this group of cases, 263 (50.1%) patients obtained excellent reconstructed ears with natural aesthetics; 238 (45.3%) patients obtained good outcomes, and the natural aesthetics were affected mainly due to a shallower scapha, smaller cavity of the concha, unreasonable structural proportions, or mild changes of the substructure; 24 (4.6%) patients obtained fair outcomes, and the main reasons were compression while sleeping, cartilage exposure, framework fracture, and absorption.
Explore This Issue
June 2024Complications occurred in 36 (6.8%) patients, which is lower than in the previous study (12.2%) without quantitative planning (Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;116:1-6). There were 11 patients with flap necrosis resulting in cartilage exposure in five patients, framework absorption in 10 patients, mainly due to compression while sleeping, antihelix absorption in five patients due to suture reaction, and tragus absorption in two patients due to weak fixation. Helix displacement occurred in three patients due to compression while sleeping. Helix fracture occurred in three older male patients (27, 32, and 33 years old), and their costal cartilage was partially calcified. Post-operative hematoma occurred in one patient due to incomplete hemostasis. Framework infection occurred in one patient who had undergone an unsuccessful meatoplasty 10 years ago, and the ear canal had atresia just one month prior.