rotational flap filling the prior defect (right).[/caption]
Explore This Issue
December 2022Using a tubeless spontaneous ventilation technique, microsuspension direct laryngoscopy was performed with a Lindholm laryngoscope. A CO2 laser via micromanipulator Digital AcuBlade micromanipulator was used to create a medially based mucosal and subcutaneous tissue U-shape flap along the medial surface of the arytenoid.
Dissection was continued just lateral to the trough with care not to buttonhole the mucosa. A laryngeal flap elevator was used to tunnel a pocket underneath the trough, helping to medialize it. In some individuals, the mucosa was tightly adherent to the arytenoid, and the laser was used to slice a sliver of the arytenoid to create the pocket.
Next, the mucosa is removed off the lateral portion of the flap, using the CO2 laser, to minimize the risk of a postoperative mucocele. The lateral edges of the flap are then folded and tucked deep into the pocket. This packs the trough and fills the posterior glottic aperture. The flap is tacked in a folded position endoscopically with 6–0 VICRYLsuture on a S-28 needle. Key steps of the surgery are included in video format (see supporting video).
If there is bilateral PGI, the procedure can be staged. Concurrent bilateral flaps should be reserved for older patients with adequate airway caliber, whereas the flaps should be sequentially staged in younger children to avoid airway compromise and the need for tracheostomy. Postoperatively, the patient is admitted for overnight observation. No perioperative antibiotics are used, and antireflux medications are not routinely given unless there is a previous diagnosis of gastroesophageal reflux.
RESULTS
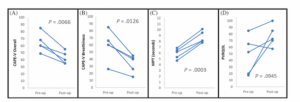
Figure 2. Results demonstrating significant improvement in (A) Consensus Auditory Perceptual Evaluation of Voice (CAPE-V)
overall, (B) CAPE-V breathiness, and (C) maximum phonation time (MPT); (D) Pediatric Voice Related Quality of Life (PVRQOL) trended toward improvement without statistical significance.
Five patients with PGI underwent the endoscopic posterior rotation flap, three of which were bilateral. The mean follow-up period between surgery and obtaining postoperative data was 70 days (range 20–160). No adverse events were encountered. In all cases, endoscopic visualization demonstrated significant improvement in PGI (Figure 1). Findings shown in Figure 2 demonstrated significant improvement in CAPE-V overall (P = 0.0066), CAPE-V breathiness (P = 0.0126), and MPT (P = 0.0003). PVRQOL trended toward improvement without statistical significance (P = 0.0945).