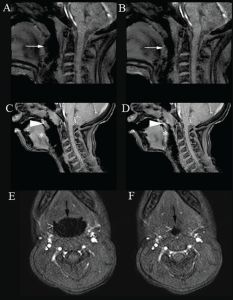
Figure 1. Cine magnetic resonance imaging showing upper airway obstruction. Sagittal images demonstrate the open (A, C) and narrowed airway (B, D) at the level of the tongue base (white arrow) and velum (arrow head)/tongue base (*). Posterior displacement of the tongue also caused posterior displacement of the soft palate (A, B). Axial images show the open (E) and narrowed airway (F) at the level of oropharynx/lateral walls (>) and tongue base (black arrow). Imaging technique prevents presentation of an example of concurrent obstruction at the level of the velum/oropharynx/lateral walls/tongue base in a single image.
Copyright 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
Figure 1. Cine magnetic resonance imaging showing upper airway obstruction. Sagittal images demonstrate the open (A, C) and narrowed airway (B, D) at the level of the tongue base (white arrow) and velum (arrow head)/tongue base (*). Posterior displacement of the tongue also caused posterior displacement of the soft palate (A, B). Axial images show the open (E) and narrowed airway (F) at the level of oropharynx/lateral walls (>) and tongue base (black arrow). Imaging technique prevents presentation of an example of concurrent obstruction at the level of the velum/oropharynx/lateral walls/tongue base in a single image. Copyright 2017 The American Laryngological, Rhinological and Otological Society, Inc.
ENTtoday - https://www.enttoday.org/article/cine-mri-dise-equally-effective-identifying-upper-airway-obstruction-children/ent_0517_pg6a/